Court marriage has become an increasingly popular choice for couples in Nepal seeking a legally recognized union without the complexities of traditional ceremonies. Whether you’re a Nepali citizen or a foreign national looking to marry in Nepal, understanding the legal framework and having the right legal representation is crucial for a smooth process.
At Haven Law Group, we specialize in guiding couples through every step of the court marriage process, ensuring compliance with all legal requirements while protecting your rights and interests.
Understanding Court Marriage in Nepal
What is Court Marriage?
Court marriage in Nepal is a civil marriage conducted and registered at the District Court, governed by the Muluki Civil Code, 2074 (2017). This legal procedure provides a valid alternative to traditional religious or cultural marriage ceremonies, offering a straightforward, legally binding union recognized both nationally and internationally.
Legal Framework Governing Court Marriage
The primary legislation governing court marriages in Nepal includes:
- Muluki Civil Code, 2074 (2017) – Chapter on Marriage
- Muluki Civil Procedure Code, 2074 (2017)
- National Civil Code (Mulki Ain) provisions
- Marriage Registration Act, 2028 (1971)
These laws establish the eligibility criteria, procedural requirements, and legal validity of court marriages conducted within Nepal’s jurisdiction.
Why You Need a Specialized Court Marriage Lawyer
Court marriage in Nepal involves multiple legal intricacies that require professional expertise. A qualified court marriage lawyer ensures:
- Proper documentation and verification
- Compliance with age and consent requirements
- Handling of inter-caste or inter-religious marriages
- International marriage complications
- Translation and notarization of foreign documents
- Representation in court proceedings
Protecting Your Legal Rights
An experienced attorney safeguards your interests by:
- Verifying the legal capacity of both parties to marry
- Ensuring voluntary consent without coercion
- Addressing property and inheritance implications
- Providing legal counsel on rights and obligations
- Handling any objections or legal challenges
Eligibility Criteria for Court Marriage in Nepal
Basic Requirements
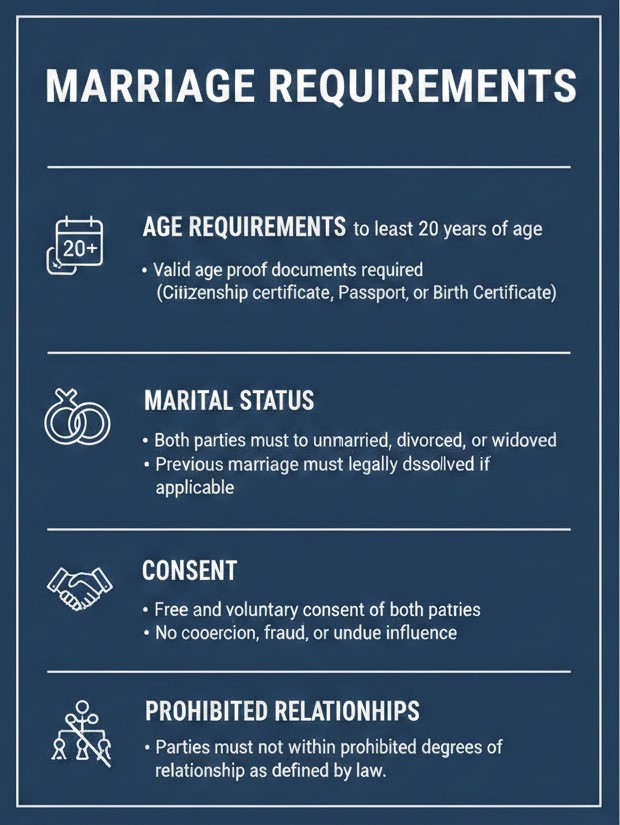
According to Section 67 of the Muluki Civil Code, 2074, the following conditions must be met:
- Age Requirements:
- Both parties must be at least 20 years of age
- Valid age proof documents required (Citizenship certificate, Passport, or Birth Certificate)
- Marital Status:
- Both parties must be unmarried, divorced, or widowed
- Previous marriage must be legally dissolved if applicable
- Consent:
- Free and voluntary consent of both parties
- No coercion, fraud, or undue influence
- Prohibited Relationships:
- Parties must not be within prohibited degrees of relationship as defined by law
Special Provisions for Foreign Nationals
Foreign nationals seeking court marriage in Nepal must comply with additional requirements:
- Valid passport and visa documentation
- No Objection Letter (NOC) or Single Status Certificate from their home country
- Legalized and translated documents
- Compliance with their home country’s marriage laws
Required Documents for Court Marriage
For Nepali Citizens
- Citizenship Certificates (original and photocopies) of both parties
- Passport-sized photographs (recent, specified dimensions)
- Unmarried/Single Status Certificate from local ward office
- Recommendation letter from local ward office
- Temporary residence certificate (if marrying outside home district)
- Divorce decree or death certificate of previous spouse (if applicable)
For Foreign Nationals
- Valid Passport with current visa
- No Objection Letter/Single Status Certificate from respective embassy
- Translated and notarized documents (if not in English or Nepali)
- Proof of legal stay in Nepal
- Two witnesses with valid identification
Step-by-Step Court Marriage Process in Nepal
Step 1: Initial Consultation and Document Preparation
The process begins with a comprehensive consultation to:
- Assess eligibility and legal capacity
- Review and organize required documentation
- Address any potential legal complications
- Develop a strategic approach for your specific situation
Step 2: Application Submission
- File application at the District Court where either party resides
- Submit all required documents with proper verification
- Pay applicable court fees
- Obtain case registration number
Step 3: Court Review and Verification
The court conducts:
- Document verification and authentication
- Background checks on marital status
- Verification of age and identity
- Assessment of free consent
Step 4: Court Hearing
- Both parties must appear before the judge
- Witnesses provide testimony if required
- Judge verifies consent and legal compliance
- Address any objections raised
Step 5: Marriage Registration
- Upon satisfaction, the court issues the marriage certificate
- Registration in official court records
- Legal validity established under Nepali law
Step 6: Post-Registration Formalities
- Obtain certified copies of marriage certificate
- Embassy registration (for foreign nationals)
- Update civil records if necessary
Timeline and Processing Duration
The standard court marriage process typically takes 3-7 working days, depending on:
- Completeness of documentation
- Court schedule and workload
- Complexity of individual cases
- Need for additional verification
Expedited services may be available in certain circumstances with proper legal representation.
Common Challenges and Legal Solutions
Documentation Issues
Challenge: Incomplete or improperly verified documents Solution: Professional legal review ensures all paperwork meets court standards before submission, preventing delays and rejections.
Age and Consent Verification
Challenge: Disputes regarding age or allegations of forced marriage Solution: Legal representation provides proper evidence and advocacy to establish legal capacity and voluntary consent.
Inter-Caste and Inter-Religious Marriages
Challenge: Family opposition or social pressure Solution: Court marriage provides legal protection, and experienced lawyers ensure your rights are protected against unlawful interference.
Foreign National Complications
Challenge: Embassy procedures and international legal compliance Solution: Specialized expertise in international marriage law facilitates smooth processing of foreign documentation.
Legal Rights and Protections After Court Marriage
Property Rights
Under the Muluki Civil Code, registered spouses enjoy:
- Equal rights to matrimonial property
- Inheritance rights as legal heirs
- Protection of individual property rights
- Legal recourse in case of property disputes
Spousal Support and Maintenance
The law provides for:
- Mutual duty of support between spouses
- Maintenance rights during marriage and after dissolution
- Legal enforcement of support obligations
Child Legitimacy and Rights
Children born from court marriage are:
- Legitimate under Nepali law
- Entitled to parental property inheritance
- Protected by child rights legislation
Marriage Registration and International Recognition
Domestic Validity
Court marriage certificates issued by Nepali District Courts are legally valid throughout Nepal and serve as conclusive proof of marriage for all legal purposes.
International Recognition
For international recognition:
- Apostille certification (for Hague Convention countries)
- Embassy legalization (for non-Hague countries)
- Certified translations for foreign authorities
Choosing the Right Legal Representation
Qualities of an Effective Court Marriage Lawyer
When selecting legal representation for court marriage, consider:
- Specialized Experience: Demonstrated expertise in family law and marriage registration
- Procedural Knowledge: In-depth understanding of court processes and documentation requirements
- Communication Skills: Clear explanation of legal rights and procedures
- Professional Network: Established relationships with court officials and relevant authorities
- Client-Focused Approach: Personalized attention to your specific circumstances
Questions to Ask Your Prospective Lawyer
- What is your experience with court marriage cases?
- How do you handle documentation verification?
- What is your approach to complex or contested situations?
- How do you ensure timely processing?
- What are your fees and payment structure?
Cost Structure and Legal Fees
Legal Representation Fees
Professional legal fees vary based on:
- Complexity of the case
- Documentation requirements
- Need for expedited processing
- Additional services required (translation, notarization, etc.)
At Haven Law Group, we provide transparent fee structures with no hidden costs, ensuring you receive value-driven legal services tailored to your needs.
Conclusion
Court marriage in Nepal offers a legitimate, efficient pathway to marital union, protected by comprehensive legal frameworks. Success depends on thorough preparation, proper documentation, and skilled legal guidance throughout the process.
Professional legal representation ensures not only compliance with procedural requirements but also protection of your fundamental rights and long-term legal interests. From initial consultation to final registration, experienced counsel navigates complexities, anticipates challenges, and secures your legal foundation for married life.
For couples seeking court marriage in Nepal, investing in qualified legal expertise represents a crucial step toward a secure, recognized, and legally protected marital union.
This article is provided for informational purposes and does not constitute legal advice. For specific legal guidance regarding your court marriage case, consult with qualified legal professionals who can address your individual circumstances.
Haven Law Group offers comprehensive legal services for court marriage, family law, and civil matters in Nepal. Our experienced team provides personalized attention to ensure your legal needs are met with professionalism and expertise.
What is the minimum age for court marriage in Nepal?
The legal age for marriage in Nepal is 20 years for both men and women, as per the Civil Code 2074 (2017). Marriages involving underage individuals are invalid and punishable by law.
How long does it take to complete a court marriage in Nepal?
On average, the court marriage process takes 2 to 4 weeks, including application filing, document verification, a mandatory 15-day public notice period, court solemnization, and certificate issuance.
Can a foreigner marry a Nepali citizen through court marriage?
Yes, foreigners can legally marry in Nepal, provided they submit a valid passport, visa, no-objection letter from their embassy, and proof of single status. Documents must be translated and notarized if not in Nepali or English.
Are witnesses required for court marriage in Nepal?
Yes, two witnesses are mandatory. They must be adults of sound mind and cannot be immediate family members of the couple.
Is registration compulsory after a court marriage in Nepal?
Yes, registration is mandatory under the Marriage Registration Act 2028 (1971). Couples must submit their court marriage certificate to the local registrar’s office to obtain an official marriage registration certificate.
Can inter-caste or inter-religion couples do a court marriage in Nepal?
Yes, court marriage is the preferred option for inter-caste and inter-religion couples in Nepal. The Civil Code 2074 (2017) guarantees the right to marry regardless of caste, religion, or ethnicity, making court marriage a legally recognized and unbiased process.
What happens if documents are not in Nepali or English?
Documents in other languages must be professionally translated into English or Nepali and notarized for court acceptance. Legal representatives can arrange certified translation services.
Is court marriage valid for visa and immigration purposes?
Court marriage certificates issued by Nepali courts are legally valid and recognized for visa applications, spouse sponsorship, and immigration purposes worldwide, subject to proper authentication.








